How Many Inches Of Asphalt Are Needed for a Driveway?
Published on: January 12, 2026 | Last Updated: April 14, 2025
Written By: George Voss
Residential driveways typically require 2-3 inches of asphalt over a 6-8 inch compacted gravel base. This thickness balances durability and cost, with installation prices ranging from $3-$7 per square foot. Exact needs depend on vehicle weight, climate, and subgrade soil strength. Thinner layers may crack under heavy trucks, while thicker ones add upfront costs but extend pavement life.
This guide breaks down asphalt thickness requirements for driveways. Learn how soil type, base preparation, and traffic patterns affect depth choices. Compare cost differences between 1.5-inch and 3-inch layers. Get tips for measuring your site and using asphalt calculators. Explore how freeze-thaw cycles and recycled materials impact design. We’ll also cover overlays, load limits, and maintenance strategies for various thicknesses.
Contents
- Typical Asphalt Driveway Thickness Guidelines
- Factors Influencing Asphalt Driveway Depth
- Calculating Asphalt Driveway Thickness
- Cost Considerations for Asphalt Thickness
- Durability and Lifespan Factors
- Comparison: Driveway Vs Parking Lot Thickness
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Closing Thoughts
- Useful References for You:
Typical Asphalt Driveway Thickness Guidelines
Driveway asphalt depth depends on use patterns, vehicle types, and base preparation. Industry standards provide clear benchmarks for long-lasting performance.
Standard Residential Driveway Thickness
Most single-family homes use 2-3 inches of asphalt over 6-8 inches of compacted aggregate base. This combination handles passenger vehicles up to 8,000 lbs. Contractors often refer to this as the “3/4 rule” – 3/4″ stone base layers under 3″ asphalt.
Minimum Asphalt Thickness for Driveways
Never install less than 2 inches of asphalt, even for light use. The Asphalt Institute specifies 2″ as the absolute minimum for any vehicular traffic. Thinner layers crack under temperature changes and develop ruts faster.
Is 1.5 Inches of Asphalt Sufficient for a Driveway?
A 1.5-inch layer fails to meet engineering standards. While some claim it works for golf carts or foot traffic, most regions require 2+ inches for code compliance. Thin installations cost 30-40% less upfront but triple repair costs within 5 years.
Is 2 Inches of Asphalt Enough for a Driveway?
Two inches serves as the baseline for asphalt thickness for driveways but needs perfect conditions:
- 8″+ gravel base with 95% compaction
- No heavy trucks/RVs
- Moderate climate (no freeze-thaw cycles)
Expect 7-10 year lifespan versus 15+ years with 3 inches.
Thickness alone doesn’t guarantee durability. Next, explore how soil quality and usage patterns affect required driveway asphalt depth.
Factors Influencing Asphalt Driveway Depth
Driveway thickness depends on multiple variables beyond basic guidelines. Proper depth prevents cracks, potholes, and premature wear while supporting vehicle loads.
Driveway Usage and Weight Considerations
Residential driveways typically handle passenger vehicles weighing under 6,000 lbs. Heavy RVs, delivery trucks, or construction equipment change requirements. Each extra 2,000 lbs increases needed thickness by 0.5-1 inch.
How Much Weight Can 3 Inches of Asphalt Support?
Three inches of compacted asphalt over 6 inches of crushed stone base holds up to 12,000 lbs per axle. This works for most single-family homes with occasional visitor vehicles. For daily dump truck traffic, increase to 4 inches with 8 inches of base.
Climate and Soil Conditions
Freeze-thaw cycles in northern states demand thicker installations. Driveways in Minnesota require 3-4 inches of asphalt, while Florida builds with 2-3 inches. Clay-rich soils need 50% more base material to prevent shifting. Sandy soils drain better but require polymer-modified binders (PG 64-28 or higher) for stability.
Base Layer Requirements
The base layer determines 60% of driveway performance. Install 4-8 inches of compacted crushed stone (1.5” minus) below the asphalt. For soft soils, geotextile fabric prevents mixing. Without proper base prep, even 4 inches of asphalt fails within 3-5 years.
Next, precise measurements ensure you order the right volume of material. Let’s explore methods to calculate exact thickness needs.
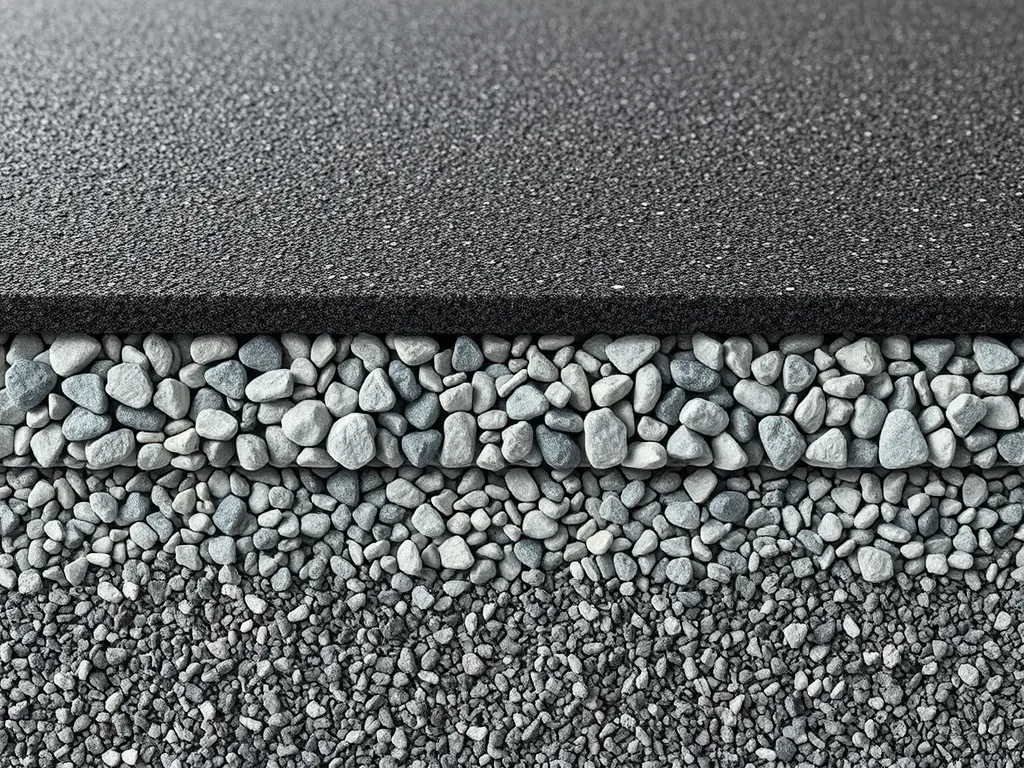

Calculating Asphalt Driveway Thickness
Proper thickness calculation ensures your driveway lasts 15-25 years. Start with precise measurements and account for vehicle types, soil stability, and local weather patterns. Most residential driveways require 2-3 inches of asphalt over a 6-inch aggregate base.
How to Measure Driveway Dimensions
Measure length and width in feet using a tape measure. For irregular shapes, break the area into rectangles. Multiply length x width for square footage. Convert thickness from inches to feet (divide by 12). A 10’x20’ driveway needing 2 inches of asphalt equals 10x20x(2/12) = 33.3 cubic feet. Divide by 27 to get cubic yards (1.23). Asphalt weighs 145 lbs per cubic foot – 1.23 cubic yards = ~2.2 tons.
Asphalt Calculator Tool Overview
Online tools like Asphalt Calculator USA simplify math. Input length, width, and desired asphalt thickness for driveways (in inches). The tool accounts for compaction rates (10-15% extra material) and base layer needs. Example: A 600 sq.ft driveway with 3-inch thickness requires 5.56 cubic yards (600 x 0.25 ÷ 27) plus 0.83 yards for compaction.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
- Measure driveway area: Length (ft) x Width (ft)
- Convert asphalt thickness to feet: Inches ÷ 12
- Calculate volume: Area x Thickness (ft)
- Convert to cubic yards: Volume ÷ 27
- Add 12% compaction buffer
- Multiply by 2.025 tons per yard
Include 6-8 inches of crushed stone base for load distribution. This prevents cracks and extends pavement life.
Accurate measurements directly affect material costs – a 12’x40’ driveway with 3-inch asphalt needs 4.44 tons ($400-$600 at $90-$135/ton). Let’s examine how thickness choices impact your budget long-term.
Also See: Cold Mix Asphalt Equipment: Cost-effective Repairs
Cost Considerations for Asphalt Thickness
Thickness impacts both initial spending and long-term savings. Balancing upfront costs with lasting functionality is key for a smart driveway investment.
Price Per Ton Of Asphalt Material
Asphalt costs $80-$120 per ton, with most driveways requiring 2-3 tons for a 3-inch layer on a 600 sq ft area. Thickness directly affects material quantity:
- 2-inch layer: 1.5-2 tons
- 3-inch layer: 2.5-3 tons
Labor adds $3-$5 per sq ft. A 3-inch asphalt driveway thickness inches setup for a standard 12’x50’ driveway runs $2,500-$4,500. Thinner layers might trim initial costs by 15%-20% but risk higher fix bills later.
Long-term Value Of Proper Thickness
A 3-inch asphalt driveway depth lasts 15-20 years with basic upkeep. Thinner 2-inch pavements often show cracks in 8-12 years. Fixing potholes or alligator cracks costs $3-$7 per sq ft – up to half the original installation price for major work.
Proper asphalt thickness for driveway projects:
- Supports 8,000-10,000 lb vehicles without rutting
- Resists freeze-thaw damage in cold zones
- Requires sealcoating only every 3-5 years
Up next: How thickness impacts how long your pavement lasts. Durability factors show why those initial inches matter.

Durability and Lifespan Factors
Driveway thickness directly affects how long your pavement lasts. Thicker layers handle daily stress better, delaying cracks and ruts. Let’s break down how inches impact performance over time.
How Long Does 2 Inches Of Asphalt Last?
A 2-inch asphalt layer typically lasts 8-15 years with routine care. Climate plays a big role: areas with freeze-thaw cycles may see 20% faster wear. Heavy vehicles like trucks accelerate surface fatigue, cutting lifespan to 5-8 years. Proper base layers (6-8 inches of compacted aggregate) extend durability by stabilizing the asphalt above.
- Mild climates: 12-15 years
- Heavy snow regions: 8-10 years
- High-traffic driveways: 5-8 years
Impact Of Thickness on Maintenance Needs
Thinner driveways demand more frequent repairs. A 2-inch surface may need crack sealing every 2-3 years, while 3-inch asphalt stretches this to 4-5 years. Thicker layers resist water penetration better, reducing pothole risks by 35-50%. Budget $0.25-$0.50 per square foot annually for upkeep on standard 2-inch driveways.
- 2-inch asphalt: Resurface every 10-12 years
- 3-inch asphalt: Resurface every 15-20 years
Thickness isn’t the only factor – next, we’ll compare residential driveways to commercial parking lots to highlight design differences.
Comparison: Driveway Vs Parking Lot Thickness
Asphalt thickness needs vary based on surface use. Driveways and parking lots face different demands, requiring distinct design specs. Let’s break down the numbers.
Typical Asphalt Thickness in Parking Lots
Parking lots use thicker asphalt layers than residential driveways. Commercial surfaces handle heavier loads and higher traffic volume. Standard parking lot asphalt includes:
| Component | Parking Lot | Driveway |
|---|---|---|
| Wearing Course | 3-4 inches | 2-3 inches |
| Base Layer | 6-8 inches | 4-6 inches |
Parking lots often add polymer-modified binders to withstand oil spills and constant turning forces. Heavy delivery trucks may require 4+ inches of asphalt over 12 inches of aggregate base.
Key Differences in Usage Requirements
Weight capacity drives design choices. A typical driveway supports passenger vehicles (3,000-6,000 lbs). Parking lots must manage:
- Daily traffic volume: 50-500+ vehicles vs 2-10 for homes
- Load types: Delivery trucks (up to 30,000 lbs axle weights)
- ESALs (Equivalent Single Axle Loads): 10,000+ vs 500 annually
Freeze-thaw regions increase base layer needs. Parking lots use 150-psi compacted stone bases versus 100-psi for driveways. Thicker asphalt alone can’t compensate for weak foundations.
Next: Learn how these specs translate to material needs with our asphalt calculator tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Add Thin Asphalt Layers Over Time?
Yes, adding thin asphalt layers, known as overlays, can be a cost-effective way to boost the surface of your driveway. However, it’s essential to ensure that the existing asphalt is in good condition, free of significant cracks or structural issues, and that the surface is adequately prepared for the new layer to adhere properly.
Does Thicker Asphalt Prevent Cracking Better?
Yes, thicker asphalt often provides better resistance against cracking. Increased thickness offers more material to absorb stress from vehicle traffic and temperature fluctuations, while also improving the overall lifespan of the driveway.
How Often Should Driveway Thickness Be Inspected?
It is recommended to inspect your driveway thickness every 2-3 years. Regular checks help identify any signs of wear, deterioration, or problem areas early, allowing for timely maintenance or repairs to prolong the life of the driveway.
Closing Thoughts
Determining the right thickness of asphalt for your driveway is crucial for durability and performance. Generally, a 2 to 3-inch thickness is recommended for residential driveways, depending on usage and soil conditions. Remember, thicker asphalt can support more weight and improve lifespan.
Make sure to assess your driveway’s specific needs. Factors like climate, intended vehicle load, and the quality of the base layer play significant roles in deciding the thickness. Special tools like the Asphalt Calculator can assist you in making precise calculations.
For more detailed information and resources, be sure to check out Asphalt Calculator USA.
Useful References for You:
- Kett, I. (1999). Asphalt Materials and Mix Design Manual. Oxford: Elsevier Science.
- How Thick Should Your Asphalt Be? – Stripe A Lot
- IAPA :: Driveways
- Is 2 inches of asphalt enough for a driveway? Asphalt Paving Thickness
- How Thick Should An Asphalt Driveway Be? – Richfield Blacktop


